Big Data
Big data refers to massive, complex datasets that traditional data processing systems struggle to handle. These datasets are characterized by high volume, velocity, and variety, requiring specialized tools and techniques for analysis.

-
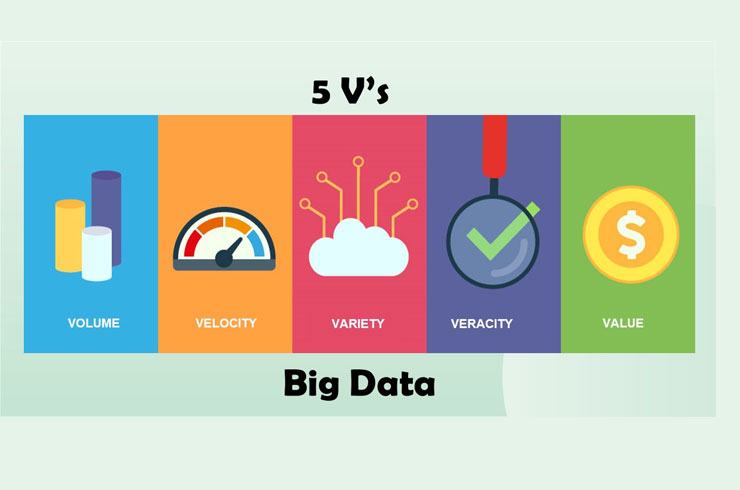
Key Characteristics of Big Data (the "3 Vs"):
Volume :
Big data involves extremely large amounts of data, often measured in terabytes, petabytes, or even larger units.
Velocity :
Data is generated and processed at high speeds, requiring real-time or near real-time analysis capabilities.
Variety :
Big data encompasses a wide range of data types, including structured (databases), unstructured (text, images, video), and semi-structured (logs, sensor data).
Veracity :
The quality and accuracy of the data are crucial, as inaccurate data can lead to flawed insights.
Value :
Big data's true value lies in the insights and knowledge that can be extracted from it through analysis.
Examples of Big Data :
Social media data :
Analyzing user posts, likes, shares, and other interactions to understand trends and sentiments.
Financial transactions :
Processing and analyzing high-frequency trading data, credit card transactions, and other financial information.
Sensor data :
Collecting and analyzing data from IoT devices, environmental sensors, and other sources to monitor and optimize systems.
Scientific data :
Handling large datasets from scientific experiments, simulations, and research.
Why is Big Data Important?
Improved Decision Making :
Big data analysis can reveal patterns and insights that lead to better business decisions.
Enhanced Efficiency :
By analyzing data on processes and operations, organizations can identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
Innovation:
Big data can drive innovation by providing new knowledge and opportunities for product development and service improvement.
Personalized Experiences :
Analyzing customer data can enable businesses to create more personalized and targeted products and services.
Competitive Advantage :
Organizations that can effectively leverage big data gain a competitive edge by making better decisions and optimizing their operations.
-


